在上一篇博客中:【推理引擎】ONNXRuntime 的架构设计,主要从文档上对ONNXRuntime的执行流程进行了梳理,但是想要深入理解,还需从源码角度进行分析。
本文以目标检测模型NanoDet作为分析的基础,部分代码主要参考:超轻量级NanoDet MNN/TNN/NCNN/ONNXRuntime C++工程记录 - DefTruth的文章 - 知乎,在此表示感谢!
OrtHandlerBase 是用来操控 ONNXRuntime 的基类,各种网络模型都可以通过继承该类进而拥有 ONNXRuntime 的使用权限,比如NanoDet;同时,NanoDet还可以扩展独属于自己的方法和成员变量,以方便推理前后的预处理和后处理工作。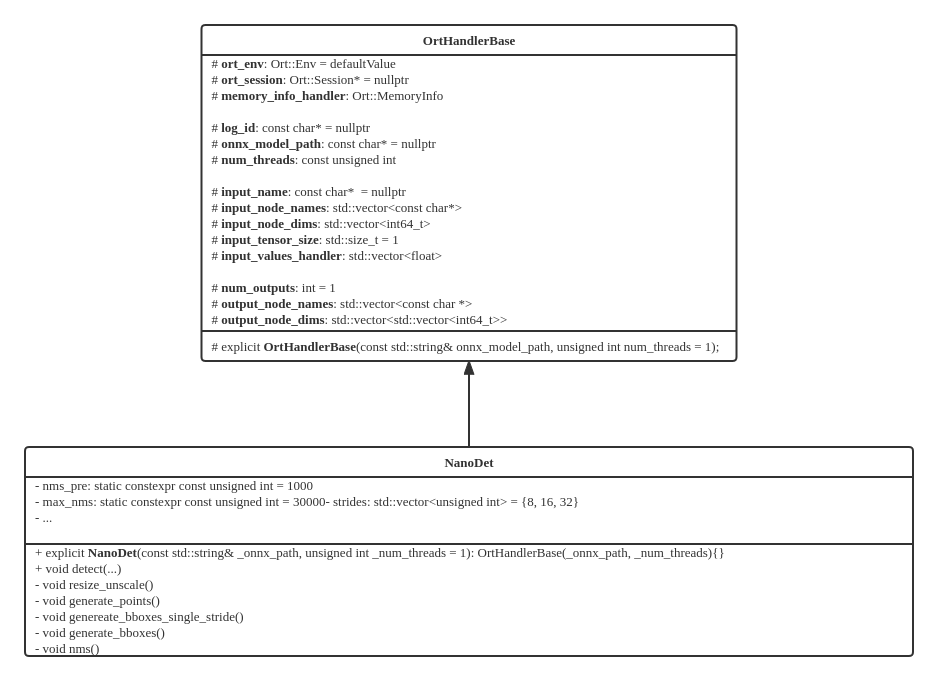
构造NanoDet对象时,会自动调用OrtHandlerBase的构造方法,在构造方法内部会首先初始化一些必要的成员变量(Ort::Env、Ort::SessionOptions),这两个变量主要用于初始化Ort::Session:
ort_env = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_ERROR, log_id); Ort::SessionOptions session_options; session_options.SetIntraOpNumThreads(num_threads); session_options.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_ALL); session_options.SetLogSeverityLevel(4); ort_session = new Ort::Session(ort_env, onnx_model_path, session_options);在构造Ort::Session 对象的过程中,会调用ONNXRuntime -> onnxruntime_cxx_inline.h 中的API:
// include/onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_cxx_inline.h inline Session::Session(Env& env, const ORTCHAR_T* model_path, const SessionOptions& options) { ThrowOnError(GetApi().CreateSession(env, model_path, options, &p_)); }GetApi() 是在 onnxruntime_cxx_api.h 中定义的:
// include/onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_cxx_api.h // This returns a reference to the OrtApi interface in use inline const OrtApi& GetApi() { return *Global<void>::api_; } // 其中 Global 的定义如下: template <typename T> struct Global { static const OrtApi* api_; };这里面主要定义了静态常量指针OrtApi*,OrtApi是在 onnxruntime_c_api.h 中定义的:
// include/onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.h // All C API functions are defined inside this structure as pointers to functions. // Call OrtApiBase::GetApi to get a pointer to it struct OrtApi; typedef struct OrtApi OrtApi; struct OrtApi{ ... // 以 CreateSession 为例: ORT_API2_STATUS(CreateSession, _In_ const OrtEnv* env, _In_ const ORTCHAR_T* model_path, _In_ const OrtSessionOptions* options, _Outptr_ OrtSession** out); // 展开ORT_API2_STATUS宏: // _Check_return_ _Ret_maybenull_ OrtStatusPtr(ORT_API_CALL* CreateSession)(const OrtEnv* env, // const char* model_path, // const OrtSessionOptions* options, // OrtSession** out) NO_EXCEPTION ORT_MUST_USE_RESULT; ... }相应地,在 onnxruntime_c_api.cc 文件中定义了 CreateSesssion 的实现:
// onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.cc ORT_API_STATUS_IMPL(OrtApis::CreateSession, _In_ const OrtEnv* env, _In_ const ORTCHAR_T* model_path, _In_ const OrtSessionOptions* options, _Outptr_ OrtSession** out) { API_IMPL_BEGIN std::unique_ptr<onnxruntime::InferenceSession> sess; OrtStatus* status = nullptr; *out = nullptr; ORT_TRY { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_ERROR(CreateSessionAndLoadModel(options, env, model_path, nullptr, 0, sess)); ORT_API_RETURN_IF_ERROR(InitializeSession(options, sess)); *out = reinterpret_cast<OrtSession*>(sess.release()); } ORT_CATCH(const std::exception& e) { ORT_HANDLE_EXCEPTION([&]() { status = OrtApis::CreateStatus(ORT_FAIL, e.what()); }); } return status; API_IMPL_END }到此,我们已经定位到CreateSession的具体实现内容,可以发现它主要由两个部分组成:CreateSessionAndLoadModel 和InitializeSession,接下来分析这两个函数。
从CreateSessionAndLoadModel 的名字就可以看出,这个函数主要负责创建 Session,以及加载模型:
// onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.cc // provider either model_path, or modal_data + model_data_length. // 也就是说,共有两种方式用来读取模型:一种是根据ONNX模型路径;另一种时从模型数据缓冲(Model data buffer)中读取,并且需要指定模型大小(Model data buffer size) static ORT_STATUS_PTR CreateSessionAndLoadModel(_In_ const OrtSessionOptions* options, _In_ const OrtEnv* env, _In_opt_z_ const ORTCHAR_T* model_path, _In_opt_ const void* model_data, size_t model_data_length, std::unique_ptr<onnxruntime::InferenceSession>& sess) { // quick check here to decide load path. InferenceSession will provide error message for invalid values. const Env& os_env = Env::Default(); // OS environment (注意:OS environment != ORT environment) bool load_config_from_model = os_env.GetEnvironmentVar(inference_session_utils::kOrtLoadConfigFromModelEnvVar) == "1"; // 创建 InferenceSession if (load_config_from_model) { if (model_path != nullptr) { sess = std::make_unique<onnxruntime::InferenceSession>( options == nullptr ? onnxruntime::SessionOptions() : options->value, env->GetEnvironment(), model_path); } else { sess = std::make_unique<onnxruntime::InferenceSession>( options == nullptr ? onnxruntime::SessionOptions() : options->value, env->GetEnvironment(), model_data, static_cast<int>(model_data_length)); } } else { sess = std::make_unique<onnxruntime::InferenceSession>( options == nullptr ? onnxruntime::SessionOptions() : options->value, env->GetEnvironment()); } // Add custom domains if (options && !options->custom_op_domains_.empty()) { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->AddCustomOpDomains(options->custom_op_domains_)); } // Finish load if (load_config_from_model) { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->Load()); } else { if (model_path != nullptr) { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->Load(model_path)); } else { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->Load(model_data, static_cast<int>(model_data_length))); } } return nullptr; }接下来深入到sess->load() 中,这里面经历了多层重载函数,最终目标是为InferenceSession的成员变量model_(ClassType: std::shared_ptronnxruntime::Model)赋值:
// onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Load(const std::string& model_uri) { std::string model_type = session_options_.config_options.GetConfigOrDefault(kOrtSessionOptionsConfigLoadModelFormat, ""); bool has_explicit_type = !model_type.empty(); // 判断是否为 ORT 类型的 Model if ((has_explicit_type && model_type == "ORT") || (!has_explicit_type && fbs::utils::IsOrtFormatModel(model_uri))) { return LoadOrtModel(model_uri); } if (is_model_proto_parsed_) { return ORT_MAKE_STATUS(ONNXRUNTIME, FAIL, "ModelProto corresponding to the model to be loaded has already been parsed. " "Invoke Load()."); } return Load<char>(model_uri); } template <typename T> common::Status InferenceSession::Load(const std::basic_string<T>& model_uri) { model_location_ = ToWideString(model_uri); // 这里定义了一个 lambda 函数 auto loader = [this](std::shared_ptr<onnxruntime::Model>& model) { LoadInterOp(model_location_, interop_domains_, [&](const char* msg) { LOGS(*session_logger_, WARNING) << msg; }); for (const auto& domain : interop_domains_) { ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR(AddCustomOpDomains({domain.get()})); } return onnxruntime::Model::Load(model_location_, model, HasLocalSchema() ? &custom_schema_registries_ : nullptr, *session_logger_); }; common::Status st = Load(loader, "model_loading_uri"); return Status::OK(); } common::Status InferenceSession::Load(std::function<common::Status(std::shared_ptr<Model>&)> loader, const std::string& event_name) { std::lock_guard<onnxruntime::OrtMutex> l(session_mutex_); // 关键代码 std::shared_ptr<onnxruntime::Model> p_tmp_model; status = loader(p_tmp_model); model_ = p_tmp_model; status = DoPostLoadProcessing(*model_); is_model_loaded_ = true; return status; }需要注意的是,onnxruntime::Model 不同于 onnxruntime::Graph,Graph 只是 Model 的一个成员变量,Model 中还包含其它基础信息,比如 version、domain、author 和 license 等内容。
在创建完 InferenceSession 后,需要进行初始化操作(InitializeSession):
// onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.cc static ORT_STATUS_PTR InitializeSession(_In_ const OrtSessionOptions* options, _In_ std::unique_ptr<::onnxruntime::InferenceSession>& sess, _Inout_opt_ OrtPrepackedWeightsContainer* prepacked_weights_container = nullptr) { // 创建 Providers std::vector<std::unique_ptr<IExecutionProvider>> provider_list; if (options) { for (auto& factory : options->provider_factories) { auto provider = factory->CreateProvider(); provider_list.push_back(std::move(provider)); } } // 注册 Providers 到 InferenceSession 中 for (auto& provider : provider_list) { if (provider) { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->RegisterExecutionProvider(std::move(provider))); } } if (prepacked_weights_container != nullptr) { ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->AddPrePackedWeightsContainer( reinterpret_cast<PrepackedWeightsContainer*>(prepacked_weights_container))); } // 初始化 InferenceSession ORT_API_RETURN_IF_STATUS_NOT_OK(sess->Initialize()); return nullptr; }接下来,深入到 InferenceSession 的Initialize() 函数中,这个函数水很深,需要分为几个小的模块来分析。
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... bool have_cpu_ep = false; // 这里使用 {} 可以提前释放 session_mutex_,不必等到退出Initialize函数才释放,可提升效率 { std::lock_guard<onnxruntime::OrtMutex> initial_guard(session_mutex_); // 判断模型是否已被加载 if (!is_model_loaded_) { LOGS(*session_logger_, ERROR) << "Model was not loaded"; return common::Status(common::ONNXRUNTIME, common::FAIL, "Model was not loaded."); } if (is_inited_) { // 判断是否已经初始化,如果已经初始化就可以直接退出Initialize函数了 LOGS(*session_logger_, INFO) << "Session has already been initialized."; return common::Status::OK(); } // 判断是否已经设置 CPU EP 来兜底,如果忘记设置,后面会自动添加 have_cpu_ep = execution_providers_.Get(onnxruntime::kCpuExecutionProvider) != nullptr; } if (!have_cpu_ep) { LOGS(*session_logger_, INFO) << "Adding default CPU execution provider."; CPUExecutionProviderInfo epi{session_options_.enable_cpu_mem_arena}; auto p_cpu_exec_provider = std::make_unique<CPUExecutionProvider>(epi); ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(RegisterExecutionProvider(std::move(p_cpu_exec_provider))); } ... }以上代码确保了 EPs(复数,多个EP,hhh) 已被正常设置(主要是CPU已经被用作兜底),接下来从 Ort 环境中读取共享的分配器(shared allocators),并更新 EPs:
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... std::string use_env_allocators = session_options_.config_options.GetConfigOrDefault(kOrtSessionOptionsConfigUseEnvAllocators, "0"); if (use_env_allocators == "1") { LOGS(*session_logger_, INFO) << "This session will use the allocator registered with the environment."; UpdateProvidersWithSharedAllocators(); // 更新 EPs } ...接下来需要设定 SessionState,需要注意:SessionState 只能被 InferenceSession 修改,
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... session_state_ = std::make_unique<SessionState>( model_->MainGraph(), execution_providers_, session_options_.enable_mem_pattern && session_options_.execution_mode == ExecutionMode::ORT_SEQUENTIAL, GetIntraOpThreadPoolToUse(), GetInterOpThreadPoolToUse(), data_transfer_mgr_, *session_logger_, session_profiler_, session_options_.use_deterministic_compute, session_options_.enable_mem_reuse, prepacked_weights_container_); ... }接下来从EPs实例中收集内核注册表(kernel registries),内核注册表分为两类:
这两类注册表的优先级并不相同,前者要高于后者。
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(kernel_registry_manager_.RegisterKernels(execution_providers_)); ... }在 KernelRegistryManager 中注册完注册表之后,开始执行非常重要的图优化,以及分割子图:
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... // add predefined transformers // 添加预先定义的变换 ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(AddPredefinedTransformers(graph_transformation_mgr_, session_options_.graph_optimization_level, saving_runtime_optimizations)); // apply any transformations to the main graph and any subgraphs // 在主图和子图上执行所有的优化Pass ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(TransformGraph(graph, graph_transformation_mgr_, execution_providers_, kernel_registry_manager_, insert_cast_transformer_, *session_state_, saving_ort_format)); // now that all the transforms are done, call Resolve on the main graph. this will recurse into the subgraphs. // 所有的图变换都已经执行完毕,然后开始递归分割子图 ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(graph.Resolve()); // Update temporary copies of metadata, input- and output definitions to the same state as the resolved graph ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(SaveModelMetadata(*model_)); ... }分割子图之后,还有一些结尾工作:
// onnxruntime/core/session/inference_session.cc common::Status InferenceSession::Initialize() { ... ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_( session_state_->FinalizeSessionState(model_location_, kernel_registry_manager_, session_options_, serialized_session_state, // need to keep the initializers if saving the optimized model !saving_model, saving_ort_format)); // Resolve memory pattern flags of the main graph and subgraph session states ResolveMemoryPatternFlags(*session_state_); // 在 session 创建完成之后,分别调用各个EP的OnSessionInitializationEnd方法,这一步主要为EP提供一个机会,进行选择性地同步或者清理临时资源 // 从而减少内存占用,确保第一次运行时足够快 if (status.IsOK()) { for (auto& xp : execution_providers_) { auto end_status = xp->OnSessionInitializationEnd(); if (status.IsOK()) { status = end_status; } } } return status; }通过上一个阶段,已经成功构造出 NanoDet 对象,接下来需要输入图像,并由 NanoDet 来执行:
// std::vector<types::BoxF> detected_boxes; cv::Mat img_bgr = cv::imread(test_img_path); nanodet->detect(img_bgr, detected_boxes);detect 函数内部:
void NanoDet::detect(const cv::Mat &mat, std::vector<types::BoxF> &detected_boxes, float score_threshold, float iou_threshold, unsigned int topk, unsigned int nms_type) { if (mat.empty()) return; auto img_height = static_cast<float>(mat.rows); auto img_width = static_cast<float>(mat.cols); const int target_height = (int) input_node_dims.at(2); const int target_width = (int) input_node_dims.at(3); // 0. resize & unscale cv::Mat mat_rs; NanoScaleParams scale_params; this->resize_unscale(mat, mat_rs, target_height, target_width, scale_params); // 1. make input tensor Ort::Value input_tensor = this->transform(mat_rs); // 2. inference scores & boxes. auto output_tensors = ort_session->Run( Ort::RunOptions{nullptr}, input_node_names.data(), &input_tensor, 1, output_node_names.data(), num_outputs ); // 3. rescale & exclude. std::vector<types::BoxF> bbox_collection; this->generate_bboxes(scale_params, bbox_collection, output_tensors, score_threshold, img_height, img_width); // 4. hard|blend|offset nms with topk. this->nms(bbox_collection, detected_boxes, iou_threshold, topk, nms_type); }其中,第 0 和 1 步是模型输入的预处理,这里不再深入介绍,想要了解可参考源码。接下来重点对第 2 步的ort_seesion->Run() 进行深入剖析。
// include/onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_cxx_inline.h inline std::vector<Value> Session::Run(const RunOptions& run_options, const char* const* input_names, const Value* input_values, size_t input_count, const char* const* output_names, size_t output_names_count) { std::vector<Ort::Value> output_values; for (size_t i = 0; i < output_names_count; i++) output_values.emplace_back(nullptr); Run(run_options, input_names, input_values, input_count, output_names, output_values.data(), output_names_count); return output_values; } inline void Session::Run(const RunOptions& run_options, const char* const* input_names, const Value* input_values, size_t input_count, const char* const* output_names, Value* output_values, size_t output_count) { static_assert(sizeof(Value) == sizeof(OrtValue*), "Value is really just an array of OrtValue* in memory, so we can reinterpret_cast safely"); auto ort_input_values = reinterpret_cast<const OrtValue**>(const_cast<Value*>(input_values)); auto ort_output_values = reinterpret_cast<OrtValue**>(output_values); ThrowOnError(GetApi().Run(p_, run_options, input_names, ort_input_values, input_count, output_names, output_count, ort_output_values)); }又到了熟悉的环节,GetApi()可参考上一章节的内容,直接到 onnxruntime_c_api.cc 中查看 Run 函数对应的实现:
// onnxruntime/core/session/onnxruntime_c_api.cc ORT_API_STATUS_IMPL(OrtApis::Run, _Inout_ OrtSession* sess, _In_opt_ const OrtRunOptions* run_options, _In_reads_(input_len) const char* const* input_names, _In_reads_(input_len) const OrtValue* const* input, size_t input_len, _In_reads_(output_names_len) const char* const* output_names1, size_t output_names_len, _Inout_updates_all_(output_names_len) OrtValue** output) { API_IMPL_BEGIN // 获取 inferencesession auto session = reinterpret_cast<::onnxruntime::InferenceSession*>(sess); const int queue_id = 0; // 模型输入:feed_names & feeds std::vector<std::string> feed_names(input_len); std::vector<OrtValue> feeds(input_len); for (size_t i = 0; i != input_len; ++i) { if (input_names[i] == nullptr || input_names[i][0] == '\0') { return OrtApis::CreateStatus(ORT_INVALID_ARGUMENT, "input name cannot be empty"); } feed_names[i] = input_names[i]; auto& ort_value = feeds[i] = *reinterpret_cast<const ::OrtValue*>(input[i]); if (ort_value.Fence()) ort_value.Fence()->BeforeUsingAsInput(onnxruntime::kCpuExecutionProvider, queue_id); } // 模型输出:output_names & fetches std::vector<std::string> output_names(output_names_len); for (size_t i = 0; i != output_names_len; ++i) { if (output_names1[i] == nullptr || output_names1[i][0] == '\0') { return OrtApis::CreateStatus(ORT_INVALID_ARGUMENT, "output name cannot be empty"); } output_names[i] = output_names1[i]; } std::vector<OrtValue> fetches(output_names_len); for (size_t i = 0; i != output_names_len; ++i) { if (output[i] != nullptr) { ::OrtValue& value = *(output[i]); if (value.Fence()) value.Fence()->BeforeUsingAsOutput(onnxruntime::kCpuExecutionProvider, queue_id); fetches[i] = value; } } // 调用 InferenceSession 的 Run 函数,执行推理 Status status; if (run_options == nullptr) { OrtRunOptions op; status = session->Run(op, feed_names, feeds, output_names, &fetches, nullptr); } else { status = session->Run(*run_options, feed_names, feeds, output_names, &fetches, nullptr); } // Run 结束后,将 fetches 中的内容取出放到 output 中 if (!status.IsOK()) return ToOrtStatus(status); for (size_t i = 0; i != output_names_len; ++i) { ::OrtValue& value = fetches[i]; if (value.Fence()) value.Fence()->BeforeUsingAsInput(onnxruntime::kCpuExecutionProvider, queue_id); if (output[i] == nullptr) { output[i] = new OrtValue(value); } } return nullptr; API_IMPL_END }进入到InferenceSession::Run 的内部:
Status InferenceSession::Run(const RunOptions& run_options, const std::vector<std::string>& feed_names, const std::vector<OrtValue>& feeds, const std::vector<std::string>& output_names, std::vector<OrtValue>* p_fetches, const std::vector<OrtDevice>* p_fetches_device_info) { std::vector<IExecutionProvider*> exec_providers_to_stop; exec_providers_to_stop.reserve(execution_providers_.NumProviders()); std::vector<AllocatorPtr> arenas_to_shrink; // 验证输入输出,并由 FeedsFetchesManager 进行管理 ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(ValidateInputs(feed_names, feeds)); ORT_RETURN_IF_ERROR_SESSIONID_(ValidateOutputs(output_names, p_fetches)); FeedsFetchesInfo info(feed_names, output_names, session_state_->GetOrtValueNameIdxMap()); FeedsFetchesManager feeds_fetches_manager{std::move(info)}; // current_num_runs_ 的类型是:std::atomic<int>,表示并行运行 EP 的数量 ++current_num_runs_; // info all execution providers InferenceSession:Run started for (auto& xp : execution_providers_) { // call OnRunStart and add to exec_providers_to_stop if successful auto start_func = [&xp, &exec_providers_to_stop]() { auto status = xp->OnRunStart(); if (status.IsOK()) exec_providers_to_stop.push_back(xp.get()); return status; }; ORT_CHECK_AND_SET_RETVAL(start_func()); } if (run_options.only_execute_path_to_fetches) { session_state_->UpdateToBeExecutedNodes(feeds_fetches_manager.GetFeedsFetchesInfo().fetches_mlvalue_idxs); } session_state_->IncrementGraphExecutionCounter(); // execute the graph ORT_CHECK_AND_SET_RETVAL(utils::ExecuteGraph(*session_state_, feeds_fetches_manager, feeds, *p_fetches, session_options_.execution_mode, run_options.terminate, run_logger, run_options.only_execute_path_to_fetches)); // info all execution providers InferenceSession:Run ended for (auto* xp : exec_providers_to_stop) { auto status = xp->OnRunEnd(/*sync_stream*/ true); ORT_CHECK_AND_SET_RETVAL(status); } --current_num_runs_; }至此,模型已经完成推理,接下来只需处理输出内容即可,对应 nanodet->detect() 函数的 3、4 部分。
本文主要介绍了InferenceSession的构造和初始化,以及模型的推理过程,可以发现其中还是蛮复杂的。由于对ONNXRuntime的源码仍然了解有限,有许多重要的部分被略过,打算接下来分别针对突破。